Ecology:
The science that studies the relationship between living organisms and non-living things. It studies the structure and function of nature.
- The word ecology is derived from Greek words i.e., “Oikos” meaning house, and “ology” means to study.
- It is the study of organisms in their natural home.
- Ecosystem is a subpart of ecology. Ecology is the study of ecosystems.
Ecosystem:
It is a geographic area where everything such as humans, animals, microorganisms, plants, environment, landscape, weather, etc. work together to form a life.
- In an ecosystem, everything is connected through a network of interactions which allows energy & nutrition to flow throughout the entire system.
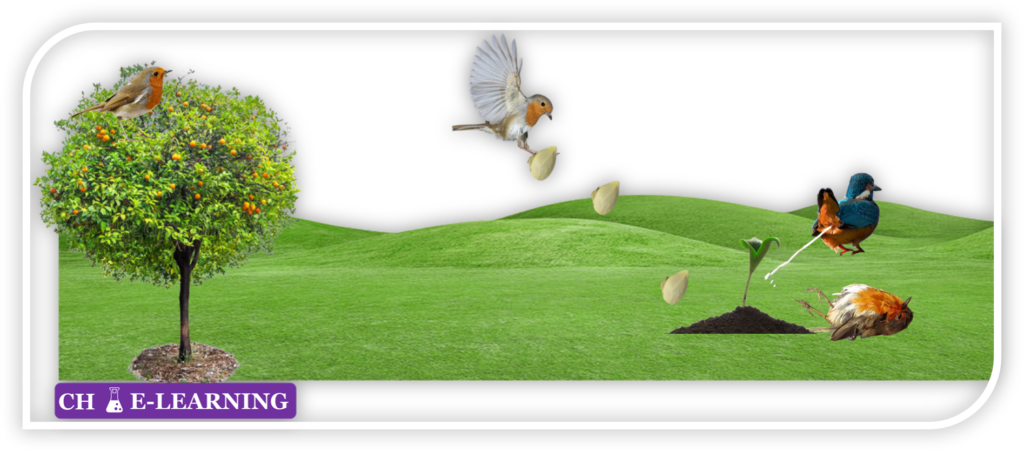

For example, the tree provides shelter and food to the birds. Birds help the tree to grow by spreading their seeds. Microorganisms create nutritious soil by decomposing dead birds and their waste. This nutritious soil is helpful in the germination of seeds.
- So, all living and non-living things together form an ecosystem.
- In other words, the network of living and non-living components in a given area is known as an ecosystem.
- It can be of any size. There are millions of different ecosystems.
- Every living and non-living thing has a role to play. All depend on each other for survival.
How the Ecosystem works:
Take the example of the pond ecosystem. It is an example of the natural ecosystem. It works on solar energy and maintains its biotic community.
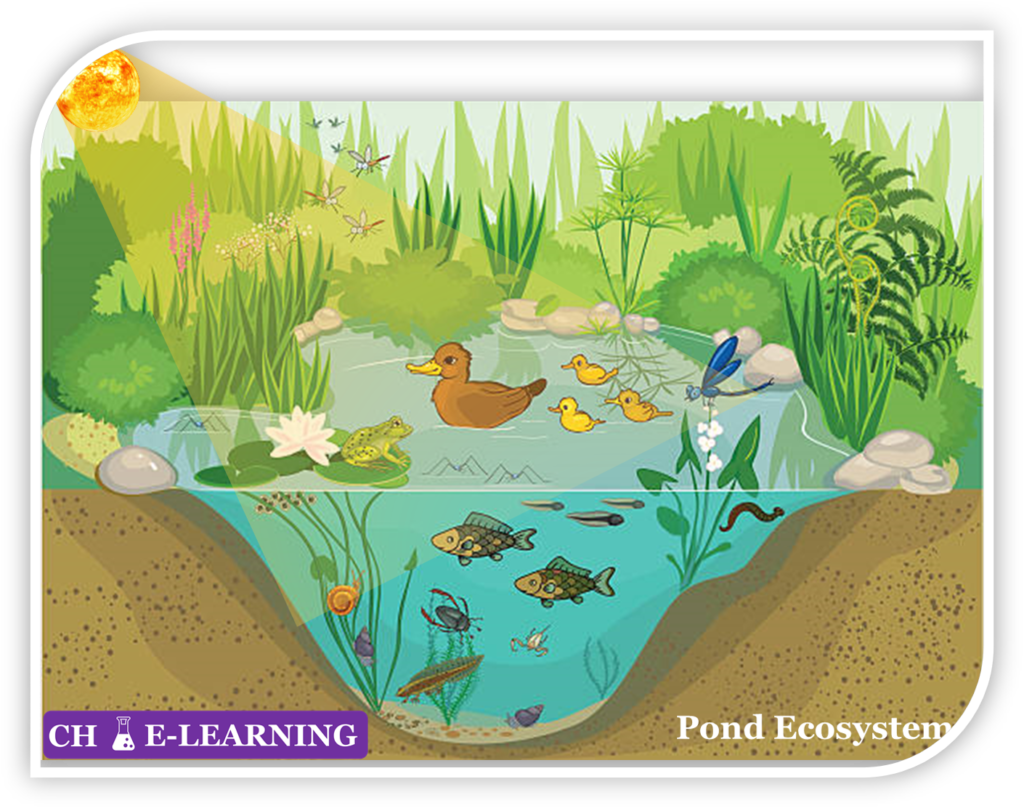
- In this system, plants growing along the border of the pond are the primary producers. They produce their own food. So, they are at the 1st tropic level of the food chain.
- These plants are eaten by insects and small fishes. So, they are at the 2nd tropic level of the food chain.
- Further, these insects & small fishes are eaten by frogs and big fishes. So, they are at the 3rd tropic level of the food chain.
- When all of these plants and animals die then they are decomposed by bacteria and fungi.
Types of Ecosystems:
There can be different types of ecosystems based on different parameters such as climate, habitats, etc.

Natural Ecosystem:
They are totally dependent on solar radiation. They are of two types.

Terrestrial Ecosystem:
Terrestrial ecosystems are found only on landforms. It has more exposure to sunlight as compared to the aquatic ecosystem. Flora and fauna are the major parts of the terrestrial ecosystem.
- Naturally occurring plants are called Flora.

- Naturally occurring animals are called Fauna.

- The terrestrial ecosystem is of different types.
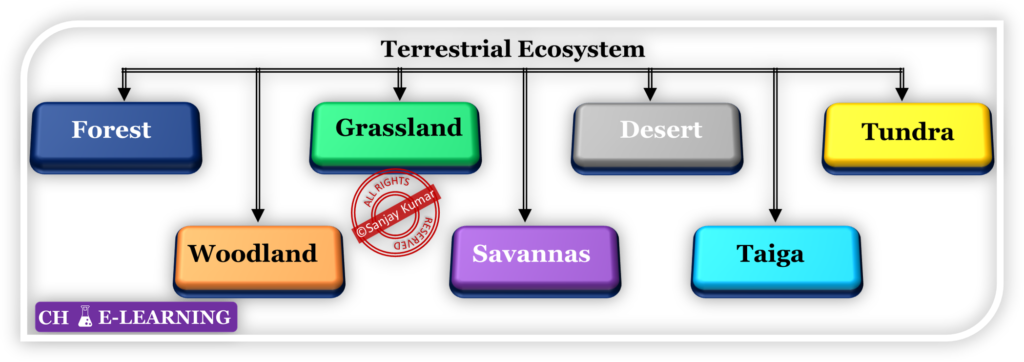
Forest Ecosystem:
These ecosystems have a dense and diverse population of living organisms. A large area of land is covered with a dense growth of trees. They cover 30 % of the earth’s surface.
- These ecosystems play important role in controlling and balancing the overall temperature of the earth. So, they are important for climate control.
As the plants absorb carbon dioxide and produce oxygen. So, they balance the oxygen level in the atmosphere.

- In the forest ecosystem, plants are the primary producer. Deer, rabbits, etc. are 2nd level consumers while lions, tigers, etc. are 3rd level consumers.
- These ecosystems are totally different from desert ecosystems. Because, unlike the desert ecosystems, they get plenty of rain. So, plants and animals in forest ecosystems don’t have to trap or store water.
Woodland Ecosystem:
These ecosystems are covered with a less dense growth of trees. They are low-density forests.
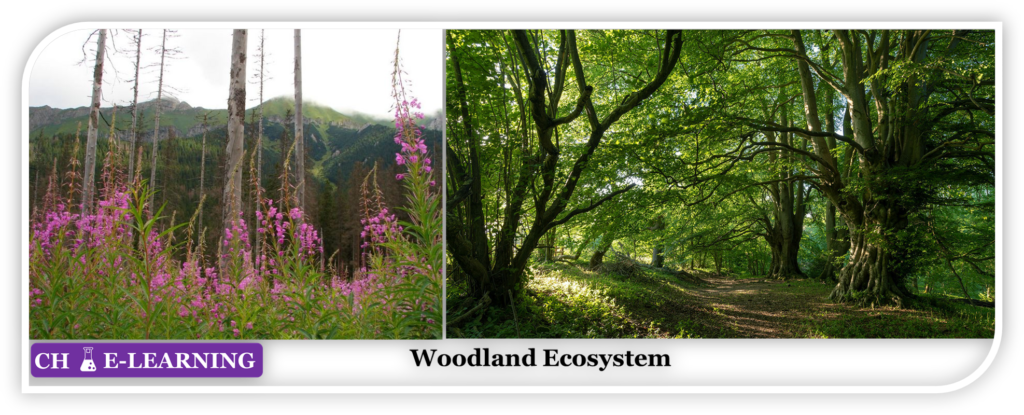

- These ecosystems are in between the dense forest and open land ecosystems.
- Due to the low-density forest, plenty of sunlight reaches the ground surface. This energy allows the animals lower to the ground to flourish.
Grassland Ecosystem:
A major area of these ecosystems is covered with grass. So, the grassland area is more than the tree-land area.
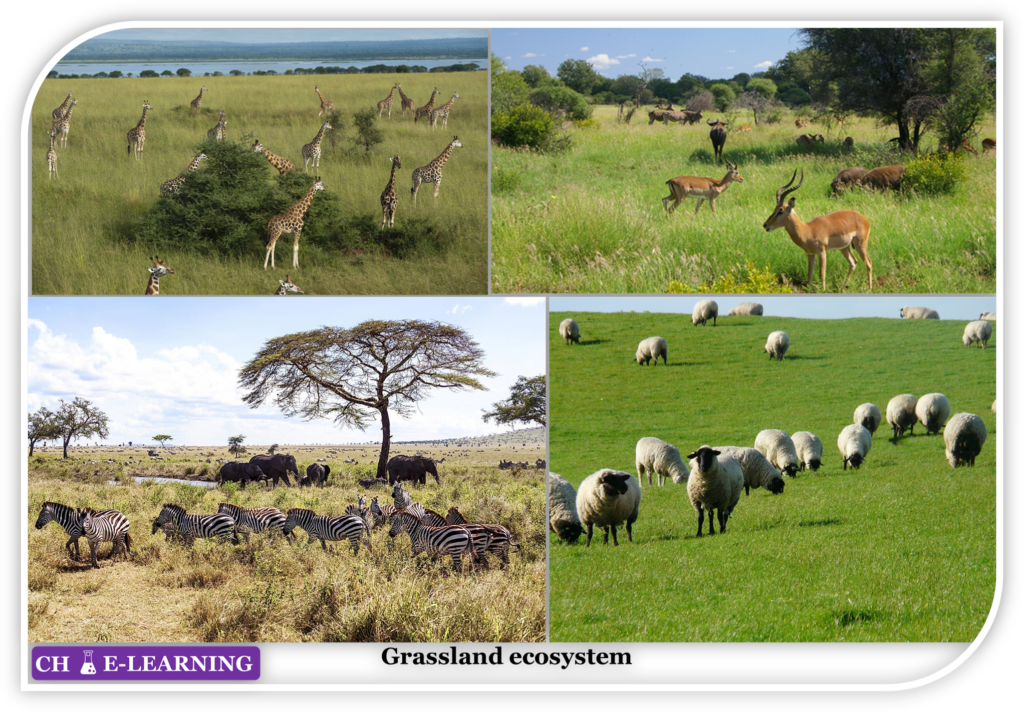

- This ecosystem mainly consists of grasses, shrubs, and herbs.
Savannas Ecosystem:
They are found in Africa. Throughout the year temperature is high.
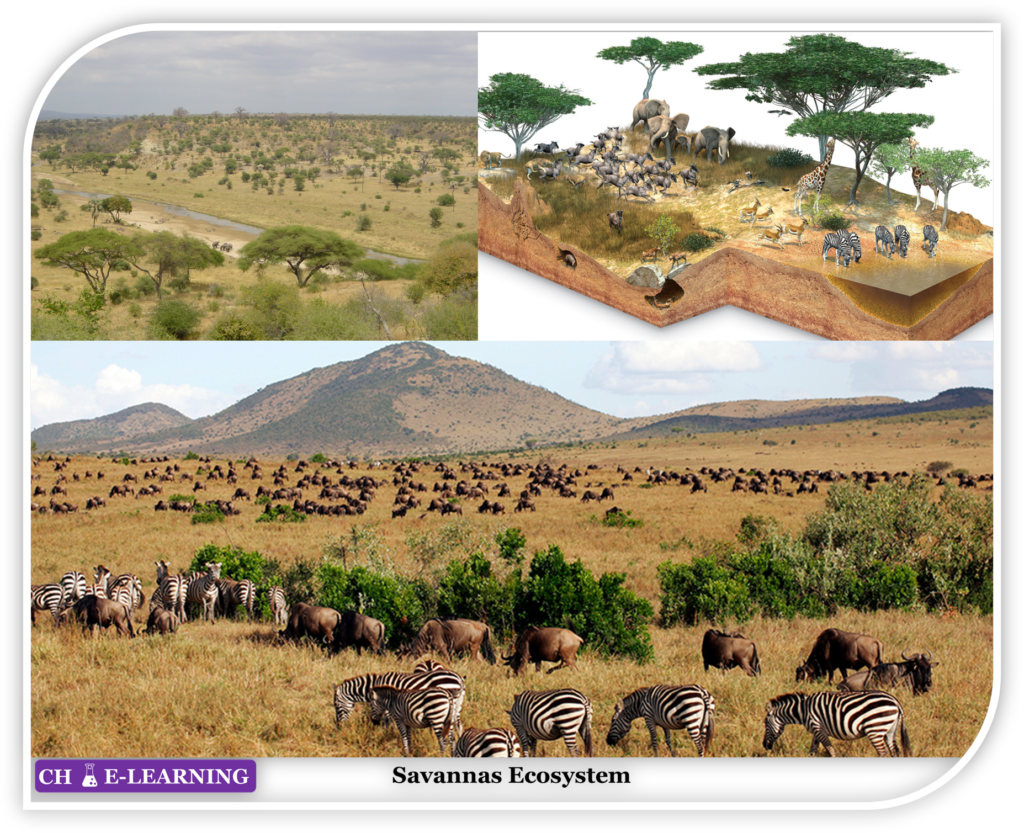

- The grass area is more with dispersed trees. A variety of organisms are part of this ecosystem.
Desert Ecosystem:
These ecosystems have a low population of flora & fauna. They cover 1/5th of the earth’s surface. They have fewer water resources.

- Due to the low population of flora and more amount of sand, they receive more heat from Sun. So, these ecosystems have high temperatures in the day time and low temperatures in the night time.
- They receive very little rain. On average, annual rainfall is less than 25 mm. So, flora & fauna have to adapt to survive without water.

- For example, a camel has the capability to store water in its bloodstream. The water inside the cactus is protected by the cactus’s special covering. This covering layer also protects it from being eaten by other creatures.
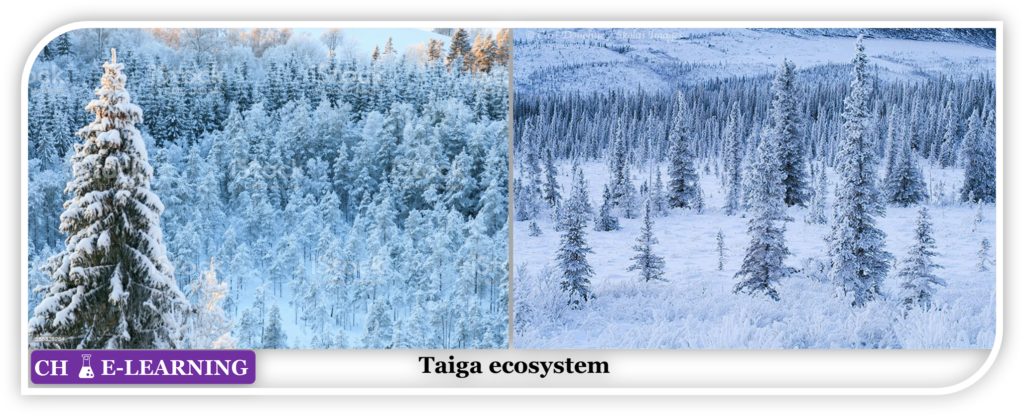
Taiga Ecosystem:
They are forests of the cold, subarctic region (Canada, Siberia, etc.). They are also called snow forests.

Tundra Ecosystem:
They are treeless regions found in the Arctic (located at the North pole) and on the tops of mountains.

- Climate is very cold. Tundra lands are covered with snow. The average temperature of the arctic tundra is -36 to -6 0C. So, only a few species of flora and fauna can live in the harsh conditions of the tundra.
Aquatic Ecosystem:
They are found in water. Millions of plants and animals live in aquatic ecosystems. Around 70 % of the earth’s surface is covered with water. They are of different types.

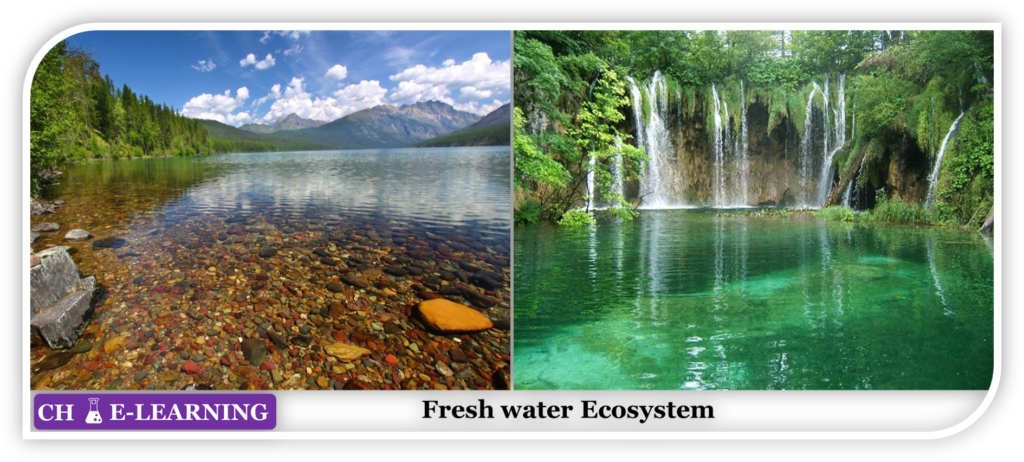
Fresh Water Ecosystem:
This ecosystem is the main source of drinking water. So, it is considered one of the essential ecosystems for humans and other living beings on land. The concentration of salt is very less in the freshwater ecosystem.

Salty water Ecosystem:
The concentration of salt is more in the salty water ecosystem. It includes coral reefs, mangrove forests, seafloor, etc.

- Coral reefs provide adequate food and shelter to marine inhabitants.


Artificial/Engineered Ecosystem:
It is man-made.
- It is fully designed and controlled by man.
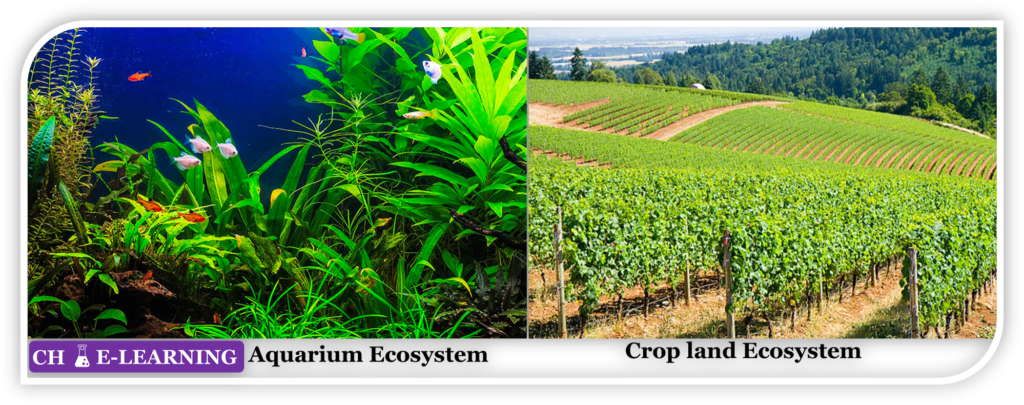

- Examples are crop land, garden, aquarium, etc.

Every time I read your posts, I learn something new. This one was no exception. Great job!
Thank you for this wonderful post! I found it very informative and engaging. Your thorough research and clear writing style made it easy to understand. I appreciate the time and effort you put into creating this valuable content. Keep up the excellent work.
Looking forward to your next post. Keep up the good work!