CPU Quiz – 1
Q 1: Water that forms scum with soap is called
Q 2: The hardness which can be removed by boiling is called
Q 3: ________ is the removal of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water.
Q 4: Which of these methods does not remove hardness?
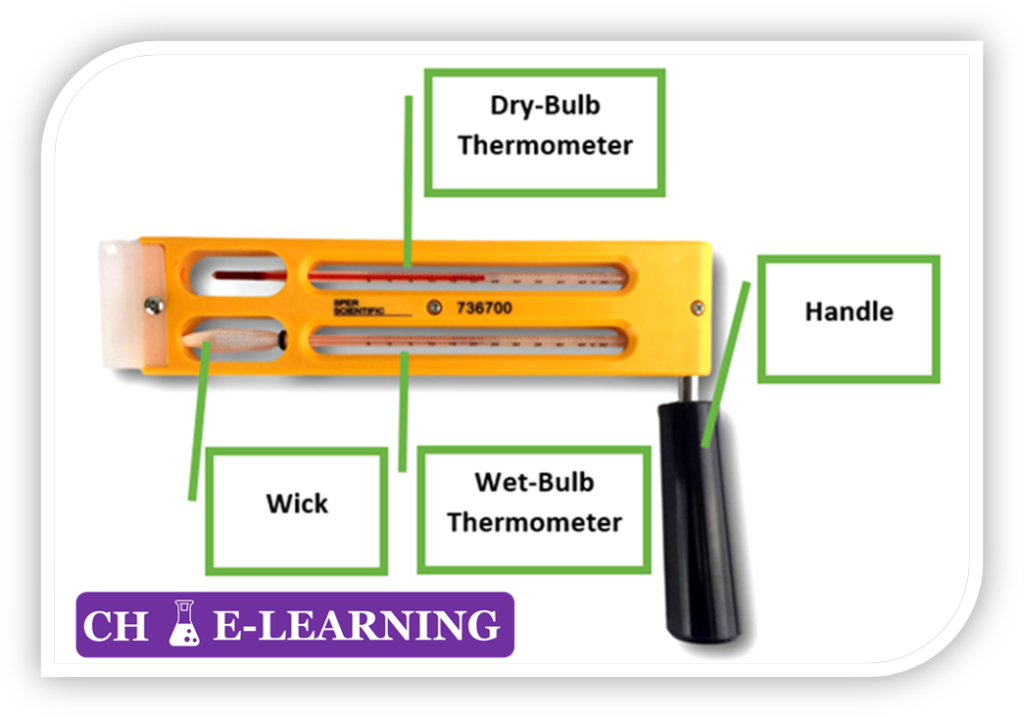
Q 5: A device used to measure humidity is called a
Q 6: Amount of water vapor in the air is regarded as.
Q 7: Humidity is the result of
Q 8: The orange color cannot be used on the surface of the cast which is not finished and left.
Q 9: Both temporary and permanent hardness of water can be removed by
Q 10: Which of the following substances are commonly used in a filter?
Pages: 1 2